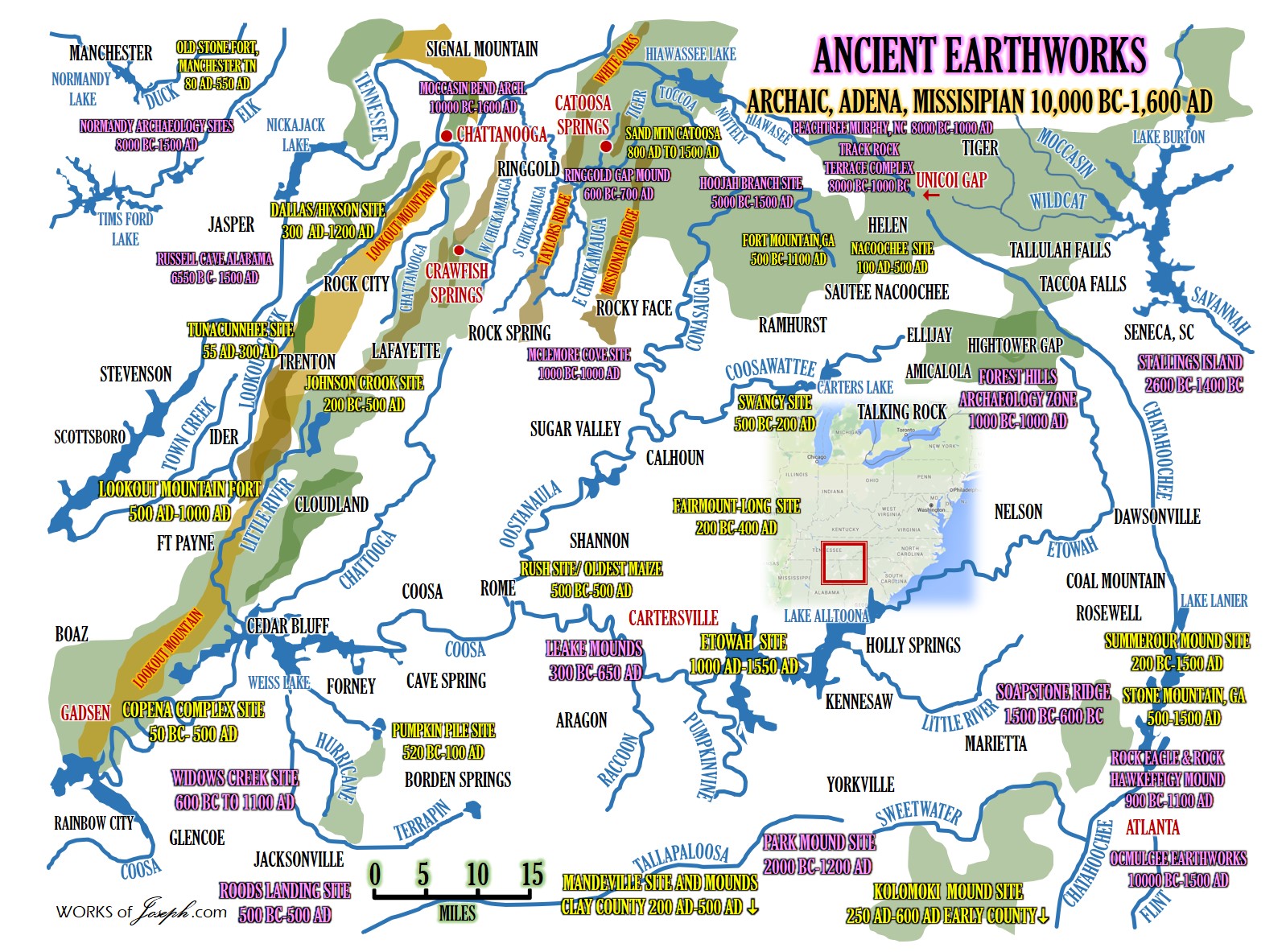
“Tunacunnhee,” according to local tradition, is the Cherokee word for Lookout Creek. It was a Hopewell Mound Site from c. 200 BC to 500 AD, and it was well known for its abundant copper panpipes, copper breastplates, and copper ear spools.
 Tunacunnhee Site upper-middle left on map in yellow
Tunacunnhee Site upper-middle left on map in yellowThe University of Georgia excavation concentrated primarily on the mounds, with the excavation of the habitation area restricted to a small area. Excavation of all four mounds was started in June of 1973. Due to time restrictions, portions of the mounds were left unexcavated with the intention of completing this work the following year, but the untimely death of Dr. Caldwell precluded further investigation of the mounds. It is hoped that in the future, circumstances will permit completion of mound excavation and a much more extensive excavation of the habitation area.
The Tunacunnhee site is of extraordinary archaeological importance for several reasons. First, it is the only well documented Hopewellian site in north Georgia. Second, the site contains the greatest variety and quantity of Hopewellian artifacts reported from the interior Southeast. Third, the excavation of the mounds provides data bearing on the long standing question of the age and cultural affiliation of stone mounds located throughout much of the Southern Piedmont (Smith 1962). Fourth, the Tunacunnhee site contains not only the widely known and excessively documented mortuary remains of a Hopewellian affiliated occupation, but an accompanying habitation area. It is one of the few examples where both the mortuary and habitation areas have been located and excavated, and offers the opportunity to examine the cultural remains of the localized, domestic aspect of a Hopewellian society.

Nephi Works in Ores
Shortly after the Nephites separated themselves from the Lamanites (establishing the land of Nephi), Nephi states that he “did take the sword of Laban, and after the manner of it did make many swords, lest by any means the people who were now called Lamanites should come upon us and destroy us.”
2 Nephi 5:14. He also writes, “I did teach my people to build buildings, and to work in all manner of wood, and of iron, and of copper, and of brass, and of steel, and of gold, and of silver, and of precious ores, which were in great abundance.” 2 Nephi 5:15.
These ores are all found in Tennessee in the area near Ducktown. The mine there has extracted over 15 million tons of copper ore in modern times. The French Huguenots enjoyed friendly relations with the Mountain Apalachee Indians, who were mining gold, copper and silver near their villages. The gold came from what is now Georgia; the silver from western North Carolina; and the copper from southeast Tennessee. To honor his friendship with these Native Americans, De Laudonniere named the region, “Les Montes Apalachiens.” Moroni’s America page 351
In 1799, gold was discovered in Cabarrus County, North Carolina, when Conrad Reed found a 17-pound “glittering stone” in Little Meadow Creek. In 1828 Dahlonega, GA was the site of the first major gold rush in the United States. Ducktown TN was the center of a major copper-mining district from 1847 until 1987. The district also produced iron, sulfur and zinc as byproducts.

In the summer of 1973, Archaeologist Joseph R. Caldwell supervised excavations at the Tunacunnhee site on the outskirts of Trenton, GA. The location is in the northwestern tip of Georgia at the foot of Lookout Mountain. Not only does it contain America’s only known stone-faced pyramid, but blends architectural traditions of both the Hopewell Culture of the Midwest and the Swift Creek Culture of the Lower Southeast.
The site goes by the name of a nearby Cherokee village from the early 1800s, Tunacunnhee, but was not built by the Cherokees. Despite this, Tunacunnhee has no meaning in Cherokee. Tunacunnhee is apparently derived from the Creek words “Tune kunhe.” There is also no “hard” evidence that the ancient village was built by the ancestors of the Creeks.
The village is believed by archaeologists to have been occupied during the Middle Woodland Period, which approximately occurred between 200 BC and 600 AD in northwestern Georgia. Tunacunnhee’s peak occupation probably was between around 100 AD and 450 AD, but this is not known for certain.
KELLOGG PHASE CHRONOLOGY. Chronological placement for the Kellogg Phase has developed through the examination of numerous sites whose data have provided both relative and absolute dates. Relative data have accumulated through the examination of stratigraphic and contextual associations of Dunlap with diagnostic artifacts representative of other cultural/temporal phases. Absolute dates have been acquired through various radio-carbon determinations . An analysis of 16 radio-carbon dates from six sites provides an overall time range for the Kellogg Phase. Including the sigmas, these dates have a range of 740 years from 20 B.C. to 760 B.C. with a mean date of 462 B.C. Seventy-five percent of the temporal span of the Kellogg Culture occurred between 300 B. C. and 600 B. C. and over ninety percent of the phase’s time span occupied the 500 year period between 150 B.C. and 650 B.C. (Bowen 1989).
CARTERSVILLE CHRONOLOGY. As noted, the Cartersville Phase can be divided into an earlier period characterized by the exclusive occurrence of check stamped ceramics and a later period distinguished by the addition of simple stamped wares. Cartersville also has been demonstrated to occur stratigraphically and immediately above Kellogg deposits (Wauchope 1948; Caldwell 1957). Radio-carbon dates for Cartersville are few and geographically dispersed. Dates from Tunacunnhee (Jefferies 1975, 1976), Cane Island (Wood 1981), Booger Bottom (Caldwell et al. 1952), and 9Fu14 (Kelly 1973; Stuart and Stuart 1969) suggest a time range beginning in the first century B. C. and continuing until the fifth or sixth century A.D. 100 BC to 600 AD
SWIFT CREEK CHRONOLOGY. Generally speaking, the Late Woodland begins at about A.D. 600 and lasts until about A.D. 900. Radio-carbon dates from key sites such as Anneewakee Creek (D02) on the Chattahoochee River south of Atlanta and from Simpsons Field (38An8) on the Savannah River in the Russell Reservoir (just across the Georgia state line in South Carolina) date the Swift Creek phase from A.D. 600 – 750. There are other earlier dates from Swift Creek sites. One such site is the Little River site in Morgan County (Mg46) where Mark Williams and Gary Shapiro (1990:82) reported dates of 100 B.C. ± 110 and A.D. 110 ± 130 from Mounds C and B, respectively. If these accurately date the Swift Creek occupation at the Little River site, then it would be earlier than most Swift Creek sites in southern Georgia or northern Florida. At Cold Springs (GelO) along the Oconee River (Wallace Reservoir–Lake Oconee), dates of A.D. 400 and 455 were obtained from a cremation on the summit of Mound B and from the last stage of Mound A. Both are considered to be Swift Creek Mounds. More recently, a Swift Creek site (M0487) at Georgia Power’s Plant Scherer was test excavated. Five radio-carbon dates spanning the period A.D. 341 – 655 were obtained from features such as postholes and pits. The average from these dates was A.D. 506, a bit earlier than is traditionally recognized as being Late Woodland (Rogers et al. 1991). 200 BC to 900 AD
Stone mounds have been reported from the Midwest that are structurally similar to the Tunacunnhee Mounds. Keller stated that the C. L. Lewis Mound, located in Shelby County, Indiana, measured 50 feet x 55 feet, and was 4.0 feet high. The mound fill was described as being two-thirds limestone and one-third earth. The Lewis mound contained Adena artifacts such as C-shaped copper bracelets, copper beads, and expanded center gorgets (Keller 1960: 398).

The Wright Mound Group, located in Franklin County, Ohio, was excavated and described by Shetrone (1925). The large mound measured 28 feet x 20 feet, and was 3.0 feet high. A stone lined pit and a burial covered with layers of stone were found in the mound, and it was reported that the entire mound was covered with a layer of earth (Shetrone 1925: 345-347).
The Copena Complex is found in the Tennessee River Valley of northern Alabama. Forty-six burial mounds an six caves containing Copena material have been reported by Walthall and Keel (1974). The mounds were described as being low conical structures of earth containing from to three to over a hundred internments. The most common burial position is extended, but cremation is also found. The number of mound structures in these sites ranges from one to eight. According to radiocarbon determination from Copena material, Copena predates Tunacunnhee by about 100-200 years. Wathall (1972) recently tested two charcoal samples that were associated with extended burials and obtained dates of A.D. 320 (1630 +65 B.P.), from the Ross site in the Guntersville Basin, and A.D. 375 (1575+75 B.P.), from the Leeman Mound, Morgan County, Alabama.
While Copena and Tunacunnhee are closely associated both temporally and spatially, each complex has certain attributes that are not shared with the other. The Tunacunnhee Mounds contained copper panpipes, copper breastplates, and small zoomorphic platform pipes, none of which has been reported from Copena sites. On the other hand, copper bracelets, copper reel-shaped gorgets, galena nodules, and large steatite elbow pipes are common in Copena sites but absent from Tunnacunnhee (DeJarnett 1952: 278).
Analysis of some of the copper artifacts from Tunacunnhee has been performed to determine the source of the copper used in the fabrication of artifacts. There is growing evidence that some of the copper used in manufacturing “Hopewellian” items found in Southeastern sites came from local sources, and analysis of copper from Tunacunnhee and other sites has tentatively demonstrated that ore from deposits in North Carolina and Tennessee was used in manufacturing some artifacts. These results were obtained by using analytical techniques including optical spectroscopy (Goad 1974: 9) and X-ray florescence (Schneider 1974).

Panpipes constitute one of the largest classes of artifacts recovered from the Tunacunnhee Mounds. A total of nine were found in association with six burials, one of the largest concentration of panpipes in the East. The only other sites with a comparable number are the Le Vesconte Mound in Ontario, Canada (Ritchie 1965: 219) and the Hopewell Mound in Ohio (Griffin et. al 1970: 99).

PREHISTORIC METAL WORKERS IN THE EASTERN UNITED STATES

PREHISTORIC METAL WORKERS IN THE EASTERN UNITED STATES
Compiled by E. Raymond Evans July, 2005 River City Research Group Chattanooga, Tennessee 37415
Tunacunnhee: A Hopewellian Burial Complex In Northwest Georgia
Panpipes, Early Metal Industries, and Cultural Association in Prehistoric North America
Richard W. Jefferies
INTRODUCTION
The following material is a reprint of the report on excavations of the Tunacunnhee Mounds at Trenton, Georgia by the University of Georgia in 1973. This is followed by some analysis concerning panpipes and other early metal artifacts with some thoughts regarding cultural association. It is hoped that this will serve to stimulate further research on this topic.


Preface
A field crew from the University of Georgia under the direction of Dr. Joseph R. Caldwell and the writer worked for ten weeks in the summer of 1973 excavating a group of stone mounds and adjacent habitation area in Dade County, Georgia. The excavation was located near Trenton, Georgia, few hundred yards east of Lookout Creek (Figure 1). The site is known as Tunacunnhee Mounds (9DD25). “Tunacunnhee,” according to local tradition, is the Cherokee word for Lookout Creek.

Figure 1.
The existence of the mounds has been known for many years, but not until the winter of 1973 was their significance recognized. The site was brought to the attention of state archaeologists from Tennessee and Mr. Pat Garrow, an archaeologist from Shorter College, by members of the Ani-yun-wiya Society, an organization of amateur archaeologists from northern Georgia and eastern Tennessee. University of Georgia archaeologists were notified of the potential importance of the site by the aforementioned people and with excellent support from a large sector of the local, community, they made plans for the excavation.
Introduction
The Tunacunnhee site may be viewed as having two parts: the mound group, located on a slightly elevated area between two limestone outcroppings against the western slope of Lookout Mountain; and the habitation area, situated on a level terrace between the creek and the mound group. The mound group covers an area of about one acre and consists of three circular limestone-mantled earth mounds (Mounds C, D, and E), a larger stone mound (Mound A), and at least two burial pits located outside the mound structures (Features 1 and 43) (Figure 1). Four additional stone mounds (Mounds B, F, G, and H), originally thought to be aboriginal, are apparently of modern origin.
Excavation of the habitation area disclosed numerous subsoil features including pits and postholes. Radiocarbon determinations and artifactual similarities indicate that the mounds and the habitation area were probably in contemporaneous use.
All of the mounds had been vandalized by pothunters over the last fifty years, most of the activity having been concentrated in the centers of the mounds. Fortunately, major damage is restricted to the mound fill and did not reach the mound bases where most of the burials and features were located. The notable exception to this was the damage done by pothunters in the winter of 1973. This digging was restricted to the southern edge of Mound C, but resulted in the destruction of t least six burials.
Description of Site and Excavation Procedure
The University of Georgia excavation concentrated primarily on the mounds, with the excavation of the habitation area restricted to a small area. Excavation of all four mounds was started in June of 1973. Due to time restrictions, portions of the mounds were left unexcavated with the intention of completing this work the following year, but the untimely death of Dr. Caldwell precluded further investigation of the mounds. It is hoped that in the future, circumstances will permit completion of mound excavation and a much more extensive excavation of the habitation area

Plate 1. Mounds C (right) and D (left) before excavation.
The three stone covered earthen mounds (C, D, and E) are located in the southwestern part of the mound group. Mound D is adjacent to the northeast edge of Mound C, while Mound E is adjacent to the southern edge of Mound C. Mound A is located approximately 100 feet northeast of the center of Mound C (Figure 1). Mound dimensions are given in Table 1.
Mound Horizontal Dimensions Height
A 37 feet N-S x 50 feet E-W 4 feet
C 31 feet N-S x 35 feet E-W 5 feet
D 12 feet in diameter 3 feet
E 25 feet in diameter 3 feet
Table 1. Mound Dimensions
Mound C
Mound C was the second largest mound of the four on the site (Plate 1) and was constructed primarily of sterile clay and covered by a one-foot-thick mantle of limestone rock (Plate II). As noted above, six burials were removed by previous excavators from the southern edge of Mound C, and two of these had associations of characteristic Hopewellian material including: a silver covered copper panpipe, four bicymbal copper ear spools, a copper breast plate, and a flint blade made from Flint Ridge, Ohio material. (Martha Otte Potter, personal communication).

Plate II. Southern and eastern sides of Mound C after removal of humus layer, showing limestone mantle.
In view of this information, it was decided to establish an east-west profile through the center of Mound C. Six 10 foot squares were excavated on the southern side of the mound to accomplish this goal. Three 10-foot squares were laid out on an east-west line to incorporate the pothunters’s trench; no additional burials or features were encountered in this area (Plate III). Excavation of the three squares immediately north of the initial 10 x 30 foot trench provided more data.
Near the center of the mound, one foot below the surface, a circular stone-lined pit was disclosed (Plate IV). Measuring 3.0 feet in diameter and 2.0 feet deep, the pit contained the partially cremated remains of a 2-3 year old child (Burial 23 – Table 2). A copper panpipe was positioned on the chest area of the burial. A drilled bear canine was also associated with the burial. The rock that formed the walls of the pit appeared to be set in a larger pit that had been dug in the top of the mound. Red clay was used to fill around the rocks and to support them in a vertical position.

Plate III. Excavation of the southern side of Mound C. The 10’x30’ excavation init in the foreground was laid out over previous excavators’ pit.

Plate IV. Rock lined pit located in the center of Mound C and containing burial 23.
The rock lined pit immediately overlay a rectangular clay platform measuring 5.4 feet x 3.1 feet, and 0.8 feet thick. An extended burial (Burial 8), oriented east-west, was encountered beneath the clay platform. A curvilinear mica cutout was located on top of the skull and additional mica was found adjacent to the skull in association with eight bone pins.
Woven Fabric, Leather, Beadwork, Copper
A central sub-mound pit measuring 6.0 feet x 10.0 feet was situated below the base of Mound C, directly under Burial 8. The pit contained sterile fill, but numerous artifacts were found on the floor of this feature (Plates V and VI). A concentration of woven fabric and what appeared to be leather was uncovered near the center of the bottom of the pit. The material had a rectangular shape and may be the remains of a bag or pouch. A copper breastplate, two sets of copper ear spools, and a copper rod with a bone handle were found between layers of the bag (Plate V). The copper had acted as a preservative, and traces of the weaving and beadwork were clearly evident on the copper surfaces. A radiocarbon determination of A.D. 150 +/- 95 years. (Uga-ML-8) was obtained from the organic material near the copper plate. The material was from the bottom the pit and represents an accurate date for initial mound construction. A perforated mica disc (Plate VI B), two human mandibles, a string of 37 shark vertebrae, a chert backed knife, drilled bear canines, and two drilled shark teeth were also recovered from the pit floor.

Plate V. Copper plate and copper ear spools in place in bottom of central sub mound pit in Mound C. Organic material removed from the surface of the copper yielded a radiocarbon determination – A. D. 150 +/- 95.


Plate VI. Copper plate (VI-A) and Mica disc (VI-B) recovered from central sub mound pit in Mound C.
Other burials were located in the fill of Mound C, as well as in stone lined basins (Table 2). Burials 14, 15A, 15B, and 15C were located in Feature 32, a stone lined basin on the northern edge of the mound. Burial 15A contained a copper panpipe, while a copper panpipe, a bird effigy platform pipe, and shell were found in association with Burial 15C.
The only ceramics directly associated with burials or mounds at the site came from the extreme northern edge of Mound C. Two small sand or grit tempered vessels with tetrapods were recovered at the base of the mound, 1.5 feet below the surface. One of the vessels was decorated with simple stamping, while the second was undecorated. These vessels have been tentatively classified as Cartersville Plain and Cartersville Simple Stamped. They are also very similar to Connestee ceramics found in North Carolina, with the exception of minor differences in paste. Connestee ceramics from western North Carolina have been found in association with Hopewellian material at Garden Creek Mound 2 (Bennie C. Keel, personal communication, 1974).
Mound E
Mound E is adjacent to the southern edge of Mound C, and on the surface the two appeared to be coalesced. It was determined that Mound C was built prior to Mound E, in that the rock facing of Mound C underlay the earth fill of Mound E.
A circular ring of red clay was discovered near the base of the mound. This characteristic was also found in the other three mounds and derives from a pit being dug in the red clay subsoil, the red clay being placed around the periphery of the pit, and the pit then being refilled with another type soil leaving the red subsoil clay as a low wall around the filled pit. A rectangular central burial pit contained an extended adult burial (Burial 17). Three copper panpipes were located on the chest of the burial (Plate VII A, B, and E). Two copper ear spools (Plate VII F), a polished stone platform pile and a large stone celt were also found in the context of Burial 17 (Plate VIII).
Mound E offered the only evidence of logs being used in the construction of a central burial pit at the site. Dark circular stains in the southern and northern profiles indicated that the pit had been covered with logs 0.5 – 1.0 foot in diameter. Excavation of the stains disclosed that the logs projected several inches into the walls of the pit. Three additional burials lacking artifact associations were located in the mound fill on the southern side of Mound E. (Table 2).
Mound D
Mound D was located on the northeast side of Mound C. The upper two feet of the mound was constructed primarily of stone. The central core of the mound was built of clay and rocks, and measured approximately 6.0 feet in diameter and 1.0 foot high. The central pit contained at least six burials. Five appeared to have been in a flexed position, but this determination was complicated by distortion caused by pressure of the rocks resting on the skeletons. No burial goods were found in direct association with these burials, but a drilled bear canine was found among the bones.


Plate VII. Copper items found in association with Burial 17 in Mound E. A, B, and E: top of three copper panpipes in burial; C and D: bottom of panpipes A and B; iron covered side of ear spools (top), and opposite side (lower).



Plate VIII. Celt and Platform pipe from Burial 17 in Mound E.
An extended burial (Burial 18F) lay in the bottom of the pit with numerous artifacts placed on and around the skeletal remains. A cache of sandstone pipes, comprising two zoomorphic platform pipes, one “monitor” platform pipe and one zoomorphic tubular pipe, was encountered at the northern edge of the pit (Plate IX A-D). In addition to these items, another sandstone platform pipe (Plate IX E) was found in the center of the pit.

Plate IX. Pipes found in association with Burial 18F in Mound D.
Other objects found in association with Burial 18F include: a three-tube copper panpipe; a four-tube silver covered copper panpipe; a copper breastplate; a mica cutout, a small band of silver; a quartz crystal projectile point; and a two-hole bar gorget.
Mound A
The construction of Mound A, located 100 feet northeast of Mound C, was quite different from that of the other three mounds. Mound A was built entirely of limestone rocks and unlike the other mounds, did not have a clay core. The rocks used in the construction of the mound weighed from a few pounds to well over 100 pounds. Mound A was excavated by starting a ten-foot-wide trench thirty feet from the southern edge of the mound and extending it northward through the center of the mound. A second ten-foot-wide trench was excavated on an east-west line so as to intersect the north-south trench in the center of the mound. A large sheet of uncut mica and a copper object resembling a small panpipe were found near a human mandible in the mound fill on the northern side of the mound. The removal of the rocks from the mound base disclosed a large central sub-mound pit. Excavation of the pit produced little except a copper ear spool and evidence of some cremated bone, found in the bottom of the pit. Two additional burials were located in rock-lined basins (Burials 11 and 19) on the northern edge of Mound A. The two basins were similar to the one containing Burials 15 A-C in Mound C.
Non-Aboriginal Stone Structures
Four mounds at the Tunacunnhee site (Mounds B, F, G and H) were originally thought to be aboriginal but later proved to be of recent origin. Construction of these four mounds was different from mounds of aboriginal origin in that the more recent mounds lacked dark humus soil on the surface of the limestone rocks and among the rocks in the interior of the mound core. Two of these mounds contained parts of a modern farm plow, and another was found to have plow scars in the sub-soil below the base of the mound. Thus, the site contained eight mounds, with four of the structures having been built around A.D. 150, and the remainder probably constructed about A.D. 1900. The situation found at the Tunacunnhee site emphasized the danger of trying to generalize about the age and origin of the numerous stone structures located in the interior Southeast.
Feature 1
Initially, an exploratory trench 10 feet wide and 100 feet long was opened between Mounds A and C, to determine whether there had been any structures or other features in the immediate vicinity of the mound complex. The squares included in the trench were excavated to the red clay subsoil, approximately one foot below surface. No structures were encountered, but Feature 1, a stone filled burial pit measuring 9.0 feet x 5.0 feet and 3.0 feet deep, was cleared at the north end of the trench (Plate X).

Plate X. Feature 1 located between Mounds A and C.
The pit contained two flexed burials, five to seven disarticulated burials, and evidence of several cremations. Grave goods were primarily utilitarian items such as: turkey bone awls; a cache of chert performs and blades; three small ground stone celts; and a drilled deer antler socket. A second feature similar to Feature 1 was located several feet to the north.
Summary of Burial and Mortuary Data
A total of thirty burials were recovered during the excavation of the Tunacunnhee Mounds by the University of Georgia (Table 2). At least six additional burials were removed from Mound C by pothunters prior to the 1973 field season. The great variety in the practices of interring bodies of the deceased was one of the more notable attributes of the Tunacunnhee site. The sample of 30 Hopewellian burials recovered during the 1973 excavations displayed significant variation in terms of the location and type of internment, as well as in the number and type of associated grave goods. Burial orientation, on the other hand, was quite consistent throughout the site. With the exception of two occurrences of north-south orientation (Burials 18D and E in Mound D), all burials were oriented east-west with the head to the east.
Burials were placed in central sub-mound pits, specially prepared stone slab lined pits or basins, the mound fill, and in pits located outside the mound structures. Extended burials composed 25 percent (n=9) and flexed burials 36 percent (n=14) of the total (N=36). The remainder of the burials (n=14) formed a residual class made up of cremations, partial burials, bundle burials, etc. There appears to be a positive correlation between extended burials located in “specially” prepared tombs and the presence of exotic Hopewellian burial goods, but this has not yet been analytically tested.
Excavation of the Habitation Area
The habitation area is located 200 yards southwest of the mound complex. The area has been subject to plowing for many years, and as a consequence the upper portion of the midden has been severely disturbed. A large number of artifacts including ceramics and lithics were recovered from the plow zone. Some midden and lower portions of features are preserved below the plow zone.
Investigation of the habitation area was considered secondary in importance to excavation of the burial mounds in the 1973 season. The limited excavation conducted here was designed primarily to determine the existence of a habitation area in the vicinity of the mounds, and to obtain sufficient data to establish its temporal and cultural relationship with the mounds. Approximately 2000 square feet of habitation area were excavated and recorded.
Features disclosed during the excavation included postholes, stone filled pits, and rounded bottom storage or refuse pits. As previously mentioned, only the lower portions of these features were intact.
One complete and one partial structure were identified during excavation of the habitation area. Structure One consisted of a circular pattern of postholes 10 feet in diameter, surrounding a rock filled pit. The postholes were approximately 0.3 foot in diameter and 2.0 feet apart. This structure may represent a sweat-house similar to that described by Wray et al (1961) for the Weaver site in Fulton County, Illinois. The rock filled pit in the center of Structure One measured approximately 5.0 feet in diameter and extended 2.5 feet below the present ground surface. The sides of the pit were fire baked red clay. Pit fill included bone, chert flakes, limestone rocks, and limestone-tempered (Candy Creek) and sand-tempered (Cartersville) ceramics.
Structure Two consisted of a roughly semicircular pattern of postholes east of Structure one. The postholes delineating Structure Two were larger in diameter and extended deeper into the subsoil than those in Structure One, suggesting a substantially larger building. Due to lack of time, only a small portion of the posthole pattern was investigated. No interior features we found in the small area of the structure that was excavated.
Preliminary analysis of the material recovered tends to support the hypothesis that the habitation area is roughly contemporary with the mounds. The supporting evidence including a radiocarbon determination of A. D. 280 +/- 125 years (Uga-ML-10) that was obtained from charcoal recovered from the undisturbed lower portion of a refuse pit. This date and the one obtained from Mound C are compatible at one standard deviation, sharing a 90 year period (A.D. 125-245) in their total combined range of A.D. 55-405. A second, apparently less instructive, date of A.D. 440 +/- 395 years (Uga-ML-9) was also obtained for the habitation area. Ceramic material found in Mound C is very similar in appearance to some of that recovered in the habitation area. Projectile points found in association with Burial 15A in Mound C are the same type (Greenville-Nolichucky) as found in the habitation area. Both copper and mica were recovered from features in the habitation area.
Intersite Analysis
A number of mounds similar to the Tunacunnhee Mounds have been excavated in the adjacent areas of Tennessee, Alabama, and North Carolina, as well as in several locations in the Midwest. Some of these mounds are constructed with stone are structurally similar to Tunnacunnhee. Others are constructed without the use of stone. Both types of mounds have been found to contain artifacts that are analogous to those recovered from the Tunnacunnhee burial mounds.
The Shaw Mound, located near Cartersville, Georgia, contained a number of artifacts that closely resemble the Tunacunnhee material. Waring (1945) reported that the Shaw Mound was a stone mound 50 feet in diameter and 10 feet high, with a roughly horseshoe shape. The mound was demolished in 1940, but the remains of an extended burial were found lying on the original ground surface. A copper breastplate, two large stone celts, and a copper celt were associated with the burial. The trapezoidal breastplate is very similar to the one found in association with Burial 18F in Mound D at Tunacunnhee.
William Webb, in his report of the survey of the Norris Basin in Tennessee, discussed several mounds that seem similar to those at the Tunacunnhee site. The Stiner Stone Mounds, located on the Powell River in Union County, Tennessee, were described as consisting of four stone mounds ranging between 16-18 feet in diameter and composed of large slabs of limestone piled directly on the clay soil. One of the mounds contained an extended adult burial oriented east-west and placed on the original surface of the ground. Three projectile points, a banded slate gorget, a sandstone pipe, two bear mandibles and large piece of mica were associated with the burial. No ceramics were found in any of the mounds (Webb 1936: 59).
A “spool shaped copper object” was recovered from a large mound in Williamson County, south of Nashville, Tennessee. Thruston (1890: 302) reported that it was found deeply imbedded in a layer of ashes and burned clay, on the original surface of the ground. Faulkner (1968) believes that this mound described by Thruston may have been one of the same mounds reported by Jennings (1946). Jennings reported a mound, located on Reid Hill, as being built on a flat hill top and measuring 18 feet high and 80 feet in diameter. The mound described by Jennings was built of stone and earth, but was essentially a stone mound (Jennings 1946: 126). Unfortunately, Thruston does not adequately describe the Williamson County Mound, so it is difficult to be sure these two accounts are referring to the same mound.
Stone mounds have been reported from the Midwest that are structurally similar to the Tunacunnhee Mounds. Keller stated that the C. L. Lewis Mound, located in Shelby County, Indiana, measured 50 feet x 55 feet, and was 4.0 feet high. The mound fill was described as being two-thirds limestone and one-third earth. The Lewis mound contained Adena artifacts such as C-shaped copper bracelets, copper beads, and expanded center gorgets (Keller 1960: 398).
The Wright Mound Group, located in Franklin County, Ohio, was excavated and described by Shetrone (1925). The large mound measured 28 feet x 20 feet, and was 3.0 feet high. A stone lined pit and a burial covered with layers of stone were found in the mound, and it was reported that the entire mound was covered with a layer of earth (Shetrone 1925: 345-347).
The Copena Complex is found in the Tennessee River Valley of northern Alabama. Forty-six burial mounds an six caves containing Copena material have been reported by Walthall and Keel (1974). The mounds were described as being low conical structures of earth containing from to three to over a hundred internments. The most common burial position is extended, but cremation is also found. The number of mound structures in these sites ranges from one to eight. According to radiocarbon determination from Copena material, Copena predates Tunacunnhee by about 100-200 years. Wathall (1972) recently tested two charcoal samples that were associated with extended burials and obtained dates of A.D. 320 (1630 +65 B.P.), from the Ross site in the Guntersville Basin, and A.D. 375 (1575+75 B.P.), from the Leeman Mound, Morgan County, Alabama.
While Copena and Tunacunnhee are closely associated both temporally and spatially, each complex has certain attributes that are not shared with the other. The Tunacunnhee Mounds contained copper panpipes, copper breastplates, and small zoomorphic platform pipes, none of which has been reported from Copena sites. On the other hand, copper bracelets, copper reel-shaped gorgets, galena nodules, and large steatite elbow pipes are common in Copena sites but absent from Tunnacunnhee (DeJarnett 1952: 278).
Analysis of some of the copper artifacts from Tunacunnhee has been performed to determine the source of the copper used in the fabrication of artifacts. There is growing evidence that some of the copper used in manufacturing “Hopewellian” items found in Southeastern sites came from local sources, and analysis of copper from Tunacunnhee and other sites has tentatively demonstrated that ore from deposits in North Carolina and Tennessee was used in manufacturing some artifacts. These results were obtained by using analytical techniques including optical spectroscopy (Goad 1974: 9) and X-ray florescence (Schneider 1974).
Panpipes constitute one of the largest classes of artifacts recovered from the Tunacunnhee Mounds. A total of nine were found in association with six burials, one of the largest concentration of panpipes in the East. The only other sites with a comparable number are the Le Vesconte Mound in Ontario, Canada (Ritchie 1965: 219) and the Hopewell Mound in Ohio (Griffin et. al 1970: 99).
Excavation of the Tunacunnhee Site has significantly increased the amount of data concerning stone mounds and Hopewell in the Southeast. The importance of the site is increased by the fact that Tunacunnhee contains not only the well documented mortuary remains of a Hopewell affiliated occupation, but also a related habitation area. The site offers the unique opportunity to further examine the cultural remains of the localized secular aspects of Hopewell.

REFERENCES CITED
DeJarnette, David L.
- “Alabama Archaeology: A Summary,” in Archaeology of Eastern United
States, edited by James B. Griffin, pp. 272-284. University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Faulkner, Charles H.
- The Old Stone Fort: Exploring an Archaeological Mystery, University of
Tennessee Press, Knoxville.
Goad, Sharon I.
1974 “Optical Spectroscopy as a Method of Archaeological Analysis,” Paper
presented at the 73rd Annual Meeting of the American Anthropological Association, Mexico City.
Griffin, James B., Richard E. Flanders, and Paul F. Titterington
1970 “Burial Complexes of the Knight and Norton Mounds in Illinois and Michigan,” Memoirs of the Museum of Anthropology, No. 2.
Jennings, James
1946 “Hopewell-Copena sites near Nashville,” American Antiquity, Vol. XII, No. 2, p. 128.
Kellar, James H.
1960 “The C. L. Lewis Mound and the Stone Mound Problem, Pre-historic Research Series Vol. III, No. IV.
Ritchie, William A.
1965 The Archaeology of New York State, The Natural History Press, Garden City.
Schneider, Kent
1974 “Results of Copper Analysis, Tunacunnhee Site, Dade County, Georgia,” Unpublished research report, Geochronology Laboratory, University of Georgia.
Shetrone, H. C.
1925 “Exploration of the Wright Group of Prehistoric Earthworks,” Ohio Archaeological and Historical Quarterly, Vol. XXXIII, No. 4, pp. 341-358.
Thruston, Gates P.
1890 The Antiquities of Tennessee, Robert Clarke Company, Cincinnati.
Walthall, John A.
1972 “The Chronological Position of Copena in Eastern States Archaeology,” Journal of Alabama Archaeology, Vol. XVII, No. 2, pp. 137-151.
Walthall, John A. and Bennie C. Keel
- “Hopewellian Trade and Interaction in the Mid-South,” Paper read at the
39th Annual Meeting, Society for American Archaeology, Washington, DC
Waring, Antonio J., Jr.
1945 “Hopewellian Elements in Northern Georgia,” American Antiquity, Vol. II, No. 2, pp. 119-120.
Webb, William S.
1938 “An Archaeological Survey of the Norris Basin in Eastern Tennessee, Bureau of American Ethnology, Bulletin 118.
Wray, Donald and Richard S. MacNeish
1961 “Hopewellian and Weaver Occupations of the Weaver Site, Fulton Co., Illinois,” Scientific Papers, Illinois State Museum, Vol. VII, No. 2.
Editors Note:
After this article was typed and sent to the author for proofreading, he suggested that the previous “Abstract” which appears on the front page of this article should be changed to “Preface” and that the following “Abstract” be added. It was impossible mechanically to insert the new “Abstract” at the beginning of the article unless the whole manuscript was retyped, thus we have included the “Abstract”
Abstract
Research carried out in the summer of 1973 disclosed the existence of a major Hopewellian habitation and mortuary site in Dade County, Georgia. The site consisted of four stone covered burial mounds, at least two burial pits located outside the mound structures and an accompanying habitation area. The site, now known as the Tunacunnhee Site ((9DD25), represents the only well documented Hopewellian site in North Georgia and contains the greatest variety and quantity of Hopewellian artifacts reported from the southeast. The site also provides data bearing on the long standing question of the age and cultural affiliation of stone mounds located throughout much of the southern piedmont.
Panpipes, Early Metal Industries, and Cultural Association in Prehistoric North America
Due largely to the unfortunate death of Dr. Joseph Caldwell, the Tunacunnhee Mound Site has not received the attention merited by its significance. The quantity and diversity of Middle Woodland material is immediately obvious to anyone who looks at the data. In addition, this site had both a mortuary, or ceremonial, and a habitation area components. The presence of scraps of copper and mica reported in the habitation area suggests that at least some of the exotic artifacts were manufactured on site.
In the case of panpipes, the excavations carried out by the University of Georgia resulted in the location of nine of these copper instruments – two of which had silver plating. Furthermore, relic collectors removed one case before the excavations and at least two after the work was completed by the University of Georgia. Two of these had silver plating. This brings the total number of panpipes from the site to thirteen. This number represents approximately ten percent of all such discoveries in the United States. This being the case, it is worthwhile to consider some facts concerning this form of artifact.
Panpipes are a musical wind instrument, consisting of graduated tubes closed at one end and fastened together. These instruments have had representatives in more non-western musical traditions around the world than any other non-percussion instrument. The player holds the instrument vertically and blows across the open end of the tubes, rather than using finger holes in a single tube as is the case with most flute like instruments. Each tube of the panpipes has its own pitch. These instruments occurred from very early times in the Middle East, Europe, China, Southeast Asia, and in North and South America.
One of the earliest mentions of such a wind instrument occurs in Gen 4:21, where we are told that Jubal was the “father of all such as handle the harp and pipe.” The Hebrew word here translated “pipe” is `ughabh. It occurs in 3 other places: Job 21:12; 30:31; Ps 150:4, and in the Hebrew version of Dan 3:5. The `ughabh was probably a primitive shepherd’s pipe or panpipe, though some take it as a general term for instruments of the flute kind, a meaning that suits all the passages cited.
In Greek and Roman mythology the god Pan was said to have invented the Panpipes by joining hollow reeds of different lengths together with beeswax and blowing into them to make music. Most of the stories connected with the origin of this instrument are connected with the god Pan and the nymph Syrinx who was changed into reeds.
In North America, panpipes were associated with the Middle Woodland Hopewellian manifestation. The Hopewellian culture, which began in Ohio and Illinois between 100 B.C. and A.D. 100, perhaps grew out of the earliera Adena culture or merged with it. Before declining sometime between A.D. 400 and 500, its influence reached across many thousands of miles, including the Southeast. Earthworks also marked the Hopewell phenomenon. Followers in the Midwest built ridges, sometimes 12 feet tall, shaped into expansive squares, circles, and octagons that could enclose as much as 80 acres. The term Hopewell has been used to describe a Middle Woodland phase in the Ohio Valley, a cultural type, or a burial complex. Stewart Streuver has suggested that the term could best apply to an interaction sphere. The Hopewellian interaction sphere involved some form of trade of gift exchange and extended from Ontario south to the Ohio and Mississippi drainage systems as far west as Arkansas and east to Florida. Major sites are usually located along rivers and tributary streams. It is considered one complex because the artifacts found in burials are made in near uniform styles from exotic raw materials such as copper, silver, obsidian, mica, and marine shells. Their dead were often accompanied by objects, such as the copper panpipes, that must have held great value for the people who buried them. (1)
It was once popular to think of “Hopewell” as a cultural manifestation that developed in the Ohio Valley directly from the earlier Adena culture. Now, however, there is evidence suggesting that Hopewellian roots may cover a much wider area. Located in Citrus County on the west coast of Florida, the Crystal River Site is the southernmost manifestation of the Hopewellian interaction sphere. Artifacts, including copper panpipes, found at Crystal River suggest that it was part of a major trade route from the Yucatan in eastern Mexico to the Ohio River Area. Two ceremonial stones called Stelae, similar to those that occur in the Mayan area of the Yucatan, but not normally found north of Mexico, are the most enigmatic features of the Crystal River Site. It is believed that these two limestone rocks were deliberately placed in an upright position by the Indians around A.D. 440. There has been speculation that the stones are placed in alignment with the soltice and equinox making it an astronomical site. (2)
In southwest Georgia, such a ceremonial focal point developed at Mandeville near the Chattahoochee River in Clay County. A flat-topped mound which once held a temple and a cone-shaped burial mound attest to the strong Hopewell influence at Mandeville. The mounds, now submerged under the waters of Lake Walter F. George, stood about 900 feet apart, with the village between them. Archeologists uncovered many artifacts in the mounds, including five panpipes. Made from hollowed river cane, four of the instruments were coated with copper; one was covered with a mixture of copper and silver. The Mandeville mounds also contained copper beads, cut mica, prismatic blades, and many ax-like tools called celts made from lustrous greenstone. (3)
Fourteen copper ear spools, all except one found in a single grave, testified to what must have been a particularly painful form of adornment. The ear spools, disk-shaped and resembling miniature cymbals, were held in place by a thin column or rivet. The wearer’s ear lobe was sliced open with a sharp rock, then the ear spool column was inserted. As the wound healed, the ear spool was sealed into place. Archeologists uncovered remnants of several smoking pipes, one with the bowl shaped like a bird. All of the pipes found at Mandeville were the platform variety, standing upright on squat, rectangular bases. The bowls are plain or shaped into bird and other animal effigies. (4)
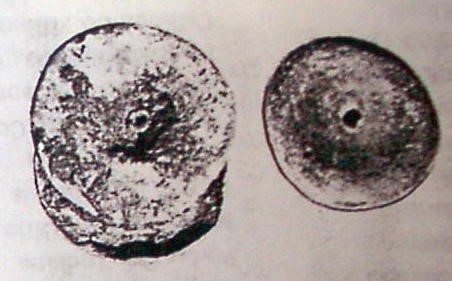
Copper ear spools.
Scientists also found several human figurines at Mandeville, both intact and in fragments. One clay figurine, about three and a half inches tall and found in the burial mound, represents a woman bent slightly forward at the waist. She wears a skirt painted red and is bare breasted. Her feet are also painted red, and she wears red arm bands. Her hair tapers down her back to the waist, and both her hair and back are painted black. There is a display in the Columbus Museum of another Mandeville woman figurine with an elaborate hairdo with two out-swept sides resembling horns. Archeologists speculate that the figurines may be sculptural portraits of the society’s elite. (5)
Further north in a western corner of Georgia near Chattanooga, Tennessee, The Tunacunnhee Site similarly reflect the same ritualism. Venerated religious leaders or priests officiated at the intricate burial ceremonies that often involved cremation and sumptuous feasts and included placing exotic artifacts with the dead. This ceremony, or religion, appears to be the glue that held the Hopewellian interaction sphere together. There may have also been a special class of traders who followed a network of trails and rivers extending hundreds of miles. As the traders sought materials near and far, they probably imparted their religious and ceremonial ideas to those they met along the way. (6)
Gloria Young, at the University of Arkansas, became interested in panpipes through the study of an example from the Helena Crossing site in Arkansas. “To see if the Helena panpipe was, as the name implies, a musical instrument,” she stated, “I reconstructed it and found that it would produce musical tones. The two outer tubes of the reconstructed Helena panpipe produce musical tones one octave apart. They are plugged with wooden and fiber plugs which determine the length of the air column. Compared to a strobotuner, the left tube produces an A ten one hundredths of a semi-tone flat, one and one half octaves above middle C. The right tube produces an A one octave higher. Recently it occurred to me to stop the middle tube with my thumb while blowing. So stopped, it produces three tones, all overtones. The tones are approximately an A one octave below the A of the left tube, an overtone four notes higher (D), and an overtone six notes higher (B).” (7)

Copper-jacketed panpipes.
A – Back of instrument: note tie marks.
B – Front of panpipes, showing silver plating at upper end.
C – Cut-away view, showing cane tubes and plugs.
[Drawing from Volume 50, Part 1,
Anthropological Papers of the American Museum of Natural History.]

Panpipe burial sites.
In 1975, Young published A Structural Analysis of Panpipe Burials. In this study she documented approximately sixty panpipes recovered from twenty-three sites ranging from the Le Vesconte site in Northumberland County, Ontario to the Crystal River site in Citrus County, Florida. It should be noted that at the time when she did this study data from the Tunacunnhee Mounds Site was not available to her. In spite of the wide distribution of these items, and the fact that the burials had a great diversity in style, she found that all had “an astonishing similarity of both style and material.” (8)
“All of the casings were of annealed metal,” she stated, “corrugated in front, flat and lapped in back, covering three or four tubes of cane or bone. All specimens except that from Baehr were from one and one half to two and one-fifty inches wide. This is apparently because the wild cane, Arundaria, grows consistently to a diameter of one half inch in mature stalks. Panpipes with little material between the tubes will be close to one and one-half inches wide, those with yarn or clay in the interstices will be wider, especially if they have been crushed somewhat by the weight of the earth. Panpipes varied more in length, which would have been musically unimportant since the tones produced depended not on the length of the tubes but that of the inner plugs.” (9)
The similarity of these panpipes have led some to speculate that they were all manufactured in one place and diffused to various parts of the Hopewellian interaction sphere. Young, however, has pointed out that: “With the possible exception of the Turner central altar panpipe (made of meteoric iron) and the Hopewell Mounds 20 panpipe, which has bone tubes, the panpipes could not have been made from purely local materials in any one place. Several of the casings have been analyzed and show that the metal from which they are made came from Isle Royale and the Lake Superior region or from Cobalt, Ontario. The northernmost range of the only North American cane, Arundaria, may be delimited by a line running from the southwest corner of Missouri through Cape Girardeau, up the Ohio River valley to just past Cincinnati, then eastward to Virginia (See figure 2). [Figure 2 is the map shown above.] The panpipes, then, are a blending of resources from the north and south of the interaction sphere. They, like the sphere itself, represent the transcending of regional and burial style differences and seem to have provided a bond between the inhabitants along thousands of miles of inland waterways. The Hopewell style panpipe of metal and cane, a variation of what is believed to be a very ancient type of musical instrument, could not have developed before the rise of the interaction sphere brought the raw materials together. As unique representatives of that specific interaction sphere, it is not unusual that they disappeared with its wane.” (10)
Although the manufacture of metal panpipes seems to have ended with the decline of Middle Woodland, the Native metal industry did not. A small, but significant copper industry continued in the Southeastern United States up to the time of European contact. At sites like Etowah in Georgia, sheet copper plates with engraved or embossed designs are well known from the Mississippian occupation. Similarly, in the Chattanooga area, elite individuals living on the Dallas/Hixon Sites wore copper ear spools that are virtually identical to those worn more than a thousand earlier at the Tunacunnhee Site. (11)
The earliest Europeans in North America found that copper ornaments were highly prized by the Native peoples. Sir Ralph Lane, an English soldier who visited Native towns in North Carolina in 1584, observed: “The mineral they say is Wassador, which is copper, but they call by the name Wassador every metal whatsoever: they say it is of the color of our copper [brass], but our copper is better than theirs: and the reason is for that it is redder and harder.” (12)
Since copper was the only metal they knew when they came in contact with Europeans, it is logical that they would use their word for copper to apply to all metals. Not only did they not differentiate between brass and copper, but, when questioned by the Spaniards about gold, they assumed copper to be the metal in question. When Hernando de Soto asked the Koasatis on the French Broad River in 1540 where gold could be found, he was told that the province to the north, Chisca (now known to be Yuchis) had much wealth, including gold. The control of large salt springs near the present Saltville, Virginia and a knowledge of working copper gave the Yuchis in the Chisca area a tremendous economic advantage in dealing with their neighbors. (13)
The early Europeans found a trail, called the Great Trading Path, that extended from the mountains of western North Carolina to the present city of Augusta, Georgia. This trail was known as “The Occaneechi Trading Path.” The primary commodities traded along this route The English regarded “Occaneeachi” as a ‘tribal’ or ethnic designation. The word, however, is an Algonquian term meaning simply “a place where people gather.” (14)
Robert Beverly wrote that there was a “general sort of language,” that he called “Occaneachi.” This language, “which is understood by the chief men of many nations as Latin is in most parts of Europe… The general language here used is said to be that of the Occaneechees, though they have been but a small nation, ever since those parts were known to the English.” He added that this ‘language’ was used by priests in religious ceremonies throughout Virginia “as the Catholics of all nations do their mass in Latin.” Years later, a remnant of this ‘language’ was analyzed and found to contain fragments of Siouan, Algonquian, and Iroquois words, suggesting a form of trade jargon used in business transactions among speakers of different languages. (15)
As will be shown below, a highly valued copper artifact from the contact period was a large copper disc. When polished, it is easy to see that such an item would have been a symbol for the sun. By extension, it is also reasonable that copper would have been regarded as the metal of the sun. The Yuchis were known by many different names given them by other groups. They, however, called themselves Tsoyaha, meaning “Children of the Sun,” a name that could also imply “Workers in Copper.” (16)
Rene de Laudonniere, the leader of the abortive French colony in Florida during the early 1560’s, wrote that the leaders of the Timucuan Indians wore large metal discs of copper around their necks. He added, in explaining the source of the metal, that “in the Appalachian Mountains there are copper mines.” Le Moyne, the artist who accompanied the French expedition, produced several illustrations of men wearing such discs around their neck. (17)
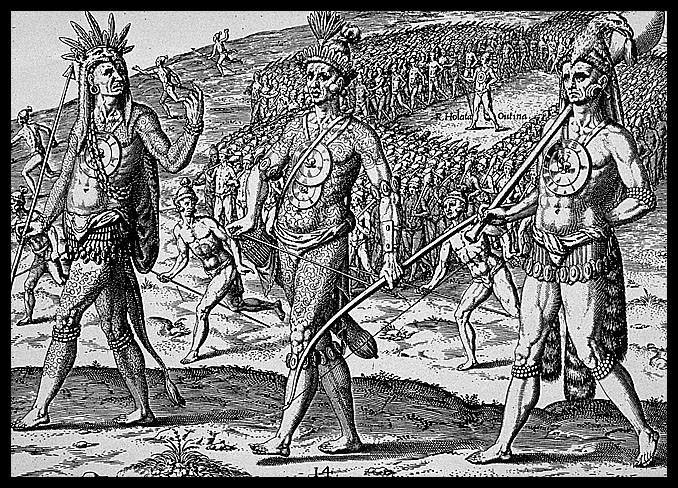

De Bry engrving of Le Moyne de Morgues, showing Timucuans wearing copper discs in Florida.
In 1584, Sir Walter Raleigh sent two English ships to explore the coast of North Carolina. One of his captains, Arthur Barlowe, later reported: “After two or three days the king’s brother came aboard the shippes…he himself had upon his head a broad plate of golde, or copper, for being unpolished we know what metal it should be, neither would he by any means suffer us to take it off his head… when… the king’s brother none durst trade but himself: except such as wear red pieces of copper on their heads like himself: for that is the difference between the noble men, and the governors of the countreys.” (18)
The English artist John White stated: “they wear a chaine of great pearles, or copper beades or smoothe bones abowt their necks, and a plate of copper hinge vpon a stringe.” Two years later, another English captain, Ralph Lane, reported that the natives obtained the copper ornaments from a powerful people in the interior known as the Mangoaks [probably Yuchis]. (19)
It would seem that the “Mangoaks,” or Yuchis, later enslaved some of the abandoned colonists from Raleigh’s so called “Lost Colony.” After the establishment of Jamestown, William Starchey wrote: “At Ritanoc, the Weroance Eyanoco preserved 7 of the English alive, four men, two boys, and one young maid (who escaped and fled up the River of Chaonoke) to beat his copper, of which he hath certain mines at the said Ritanoc.” (20)
Two men from Jamestown, Nathaniel Powell and Anas Todkill, were sent out to investigate the Mangoaks. They later reported: “…you shall find four of the English alive, left by Sir Walter Rawely which escaped from the slaughter. [They] live under the protection of a wiroane called Gapanocon, enemy to Powhaton, by whose consent you shall never recover them, [for] one of them is worth much labor.” (21)
In 1602, the Spanish king received numerous complaints against the governor of Florida from the Franciscans and others, questioning the value of the region. Hoping for an unbiased report, King Philip III ordered Don Pedro de Valdes, then governor of Cuba, to take testimony from men who were knowledgeable about the situation in Florida. One of the most interesting witnesses to testify was Juan Ribas, 60 years old, and a 40-year army veteran who had served with Pardo and Moyano. Ribas had married a Yuchi woman who had been captured in southwestern Virginia by Sergeant Moyano. The woman had the Christian name Luisa Menendez. She often talked, and had even testified on another occasion, of the beauty and riches of her homeland. Ribas stated that over the years he and his wife had often informed the Spanish authorities of the great amount of gold [actually copper], silver, and precious stones that could be found in the interior to the northwest. (22)
Another witness was Juan Lara, a soldier who was forty-six years old and had come to Florida as a child thirty-four years earlier with his father. As a youth he enlisted in the Spanish army in Florida. He stated that years ago he had gone on the expedition to Ajacan [Chesapeake Bay], 170 leagues north of San Agustin. Lara said that in Ajacan he had seen Indians with gold collars [actually copper] and that he himself had four of these valuable collars. (23)
As has been shown, a well-developed prehistoric metal industry, involving working with both copper and silver, existed in what is now the Southeastern United States going back at least to the Middle Woodland period. Sixteenth century records left by Spanish, French, and English sources indicate the primary source of copper items as being the Appalachian Mountain area. Most of the sites on which metal artifacts have been found also have stone features, either on the site or nearby.
In 1955 – 56 Philip E. Smith, with the Peabody Museum at Harvard University, conducted a study of Aboriginal Stone Constructions in the Southern Piedmont. He documented numerous stone walls, stone mounds, and stone effigies in the southern Appalachian and Piedmont regions of Georgia, Tennessee, Alabama, and parts of Kentucky and West Virginia. Some of these are well known sites, such as Fort Mountain State Park and Old Stone Fort State Park in Tennessee. As the name suggests, these features were once thought to have had a military use. This, however, is not the case. (24)
Regarding the walls at Fort Mountain, Smith stated: “It is easier to say what this wall is not than what it is… It should also be mentioned that the wall at Fort Mountain is not unique in the South, although it is the largest and most impressive found to date. A number of other stone walls have been reported and it is possible that they all belong to a very ancient complex which may have been religious or symbolic connotation… They bear certain things in common. All are of dry-stone masonry, although the quality varies greatly: most of them are built on hilltops or ridges, yet without any ostensible defensive purpose; none of them appears to have any historical background as far as white settlement is concerned. For example, there are the long Devil’s Half Acre walls in Putnam County, Georgia, which have well-fitted masonry of un-worked stone; the walls near Kensington, Georgia, (just south of Chattanooga, Tennessee,) reported by Dr. Joseph Johnson in 1955; the stone ‘fort’ at Manchester, Tennessee; the parallel walls at DeSoto Falls, Alabama; the wall on Ladd Mountain near Cartersville, unfortunately demolished some 20 years ago; the stone wall on Brown’s Mount near Macon, also demolished recently, but described by A. R. Kelly in 1938. In addition, there are unexplained lines of stone on Mount Alto, near Rome, Georgia, which seem to resemble the same type. Finally, there is a number of such structures reported from West Virginia, Kentucky and Tennessee… The widespread distribution of these phenomena leads to the suspicion that a common motif, perhaps ceremonial or symbolic, underlies them.” (25)
Considerable effort was required to construct these stone walls, and they obviously had great significance to the builders. The best hypothesis for these stone walls is that they were enclosures where different peoples gathered at regular intervals for the purpose of exchanging exotic raw materials, such as copper, silver, and mica, and possibly finished artifacts as well. This would make such sites not forts, but rather, enclosures for a kind of trade fair – something that would have been necessary for the Hopewellian interaction sphere. (26)
Following European contact, this industry continued, using brass instead of copper. The new metal was used to make some of the familiar earlier items. Brass discs were made in the same manner as the earlier copper discs. Brass C shaped bracelets replaced the earlier ones made from copper. Brass conchos have been found that are very similar to the earlier copper ear spools.
The Spaniards found the Chisca (now known to be Yuchis), living in the Appalachian Mountains were the major people working copper in the sixteenth century. It is logical to assume that their ancestors had the same role during the Middle Woodland.
References
1. Stewart Streuver, “The Hopewellian Interaction Sphere in Riverine – Western Great Lakes Culture History,” in Hopewellian Studies, edited by J. R. Caldwell and R. L. Hall, Illinois State Museum Scientific Papers, Cambridge, Vol. 12, No. 3, 1964: 85-106.
2. Crystal River, Florida State Park website.
3. National Park Service, Fort Benning, Georgia website.
4, Ibid.
5. Ibid.
6. Ibid.
7. Gloria A. Young, “Reconstruction of an Arkansas Hopewellian Panpipe,” Proceedings of the Arkansas Academy of Science, Vol. XXIV, No. 28, 1970: 28-32.
8. Gloria A. Young, “A Structural Analysis of Panpipe Burials,” Tennessee Archaeologist, Vol. 32, No. 1&2, 1976: 1-10.
9. Ibid. 7.
10. Ibid.
11. WPA/TVA Archives, presented courtesy of Frank H. McClung Museum, The University of Tennessee.
12. David Beers Quinn, Set Fair for Roanoke: Voyages and Colonies, 1584-1606, University of North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill, 1985: 111-112.
13. Charles Hudson, Knights of Spain, Warriors of the Sun, University of Georgia Press, Athens, 1997: 203; E. Raymond Evans, Napochin Shadows, Intertribal Sacred Land Trust, Chattanooga, 2003: 19; 28.
14. Lee Miller, Roanoke: Solving the Mystery of the Lost Colony, Penguin Books, New York: 200: 248-249.
15. Ibid.
16. Evans, op. cit., 19.
17. Rene de Laudonniere, Three Voyages, Translated by Charles E. Bennett, University of Alabama Press, 2001: 116.
18. Quinn, op. cit., 35-36.
19 Ibid, 111-112.
20. Miller, op. cit., 236
21. Miller, op. cit, 237.
22. Charles W. Arnade, Florida on Trial, 1593-1602, University of Miami Press, Coral Gables, 1959: 38-41.
23. Ibid.
24. Philip E. Smith, “Aboriginal Stone Constructions in the Southern Piedmont,” University of Georgia Laboratory of Archaeology Series, Paper No. 4, 1962: 1-44.
25. Ibid., 11-12.
26. Charles Faulkner, personal communication.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Arnade, Charles W.
1959 Florida on Trial, 1593-1602, University of Miami Press, Coral Gables.
Crystal River, Florida State Park website.
Evans, E. Raymond
2003 Napochin Shadows, Intertribal Sacred Land Trust, Chattanooga.
Hudson, Charles
1997 Knights of Spain, Warriors of the Sun, University of Georgia Press, Athens.
Laudonniere, Rene de
- Three Voyages, Translated by Charles E. Bennett, University of Alabama
Press.
Miller, Lee
- Roanoke: Solving the Mystery of the Lost Colony, Penguin Books, New
York.
National Park Service, Fort Benning, Georgia website.
Quinn, David Beers
- Set Fair for Roanoke: Voyages and Colonies, 1584-1606, University of
North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill.
Smith, Philip E.
“Aboriginal Stone Constructions in the Southern Piedmont,” University of Georgia Laboratory of Archaeology Series, Paper No. 4, 1962.
Streuver, Stewart
- “The Hopewellian Interaction Sphere in Riverine – Western Great Lakes
Culture History,” in Hopewellian Studies, edited by J. R. Caldwell and R. L. Hall, Illinois State Museum Scientific Papers, Cambridge, Vol. 12, No. 3, 1964.
WPA/TVA Archives, presented courtesy of Frank H. McClung Museum, The University
of Tennessee.
Young, Gloria A.
- “Reconstruction of an Arkansas Hopewellian Panpipe,” Proceedings of the
Arkansas Academy of Science, Vol. XXIV, No. 28.
- “A Structural Analysis of Panpipe Burials,” Tennessee Archaeologist, Vol.
32, No. 1&2, 1976: 1-10.http://www.examiner.com/article/where-dead-bodies-were-taken-to-be-processed